When a function accepts a value of list of values as an input, you can use operators on the values, within the function. E.g. Tag1 - Tag2.
| Operator | Description |
| + | Addition. |
| - | Subtraction. |
| * | Multiplication. |
| / | Division. |
| % | Modulus. |
| ** | Exponent or Power. |
| && | Logical AND. |
| || | Logical OR. |
| & | Bitwise or Binary AND. |
| | | Bitwise or Binary OR. |
| ^ | Bitwise or Binary XOR |
| == | Equals comparison. |
| != | Not Equal comparison. |
| < | Less Than comparison. |
| <= | Less Than or Equal comparison. |
| > | Greater Than comparison. |
| >= | Greater Than or Equal comparison |
| ! | Not comparison. |
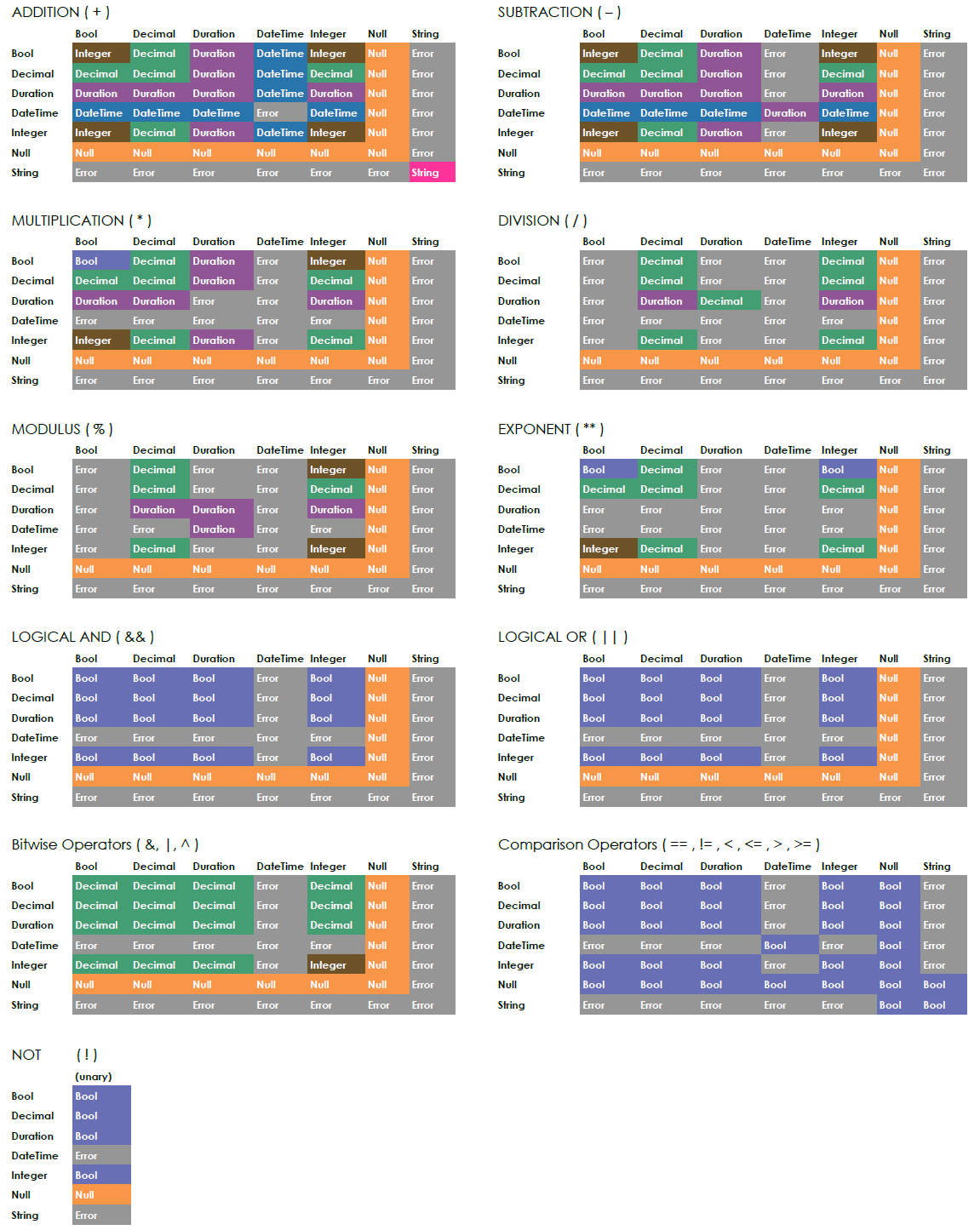
The image below shows a matrix of the operators available, and how they resolve when they are used with various data types.
Operator precedence follows the standard mathematical rules. Brackets ( ) can be used to specify precedence explicitly. E.g. 2 * (3 + 4).