ON THIS PAGE:
The Min Max process is used for testing continuous data for a monitor item. The sample data is tested against a maximum limit (Max) and a minimum limit (Min).
The process can be specified to test against both Min and Max limits, just against a Max limit, or just against a Min limit.
Events
When a new state is reached then a new event is raised. The severity for that state is specified in the state configuration for the test.
Values for the Limits
The Min and Max limits can be defined as one of the following:
- A fixed numerical value (Fixed Value)
- A variable input value defined as:
- Attribute (An attribute of the test’s source entity; this only applies where the Source Type is Entity or Hierarchy)
- Source Tag (if the test’s Source is Tag)
- Calculation
- Tag
- Entity Attribute
Optional Process Parameters
This feature allows Sentinel to use process limits of assets with missing attributes by using the UnconfiguredLimitString parameter, in the Sentinel Configuration File.
State Transition Rules
The Min Max process has clearly defined state transition logic paths. Transition from one state to another is equally dependent on the current evaluation of data, and on the current state.
State transitions cause events to be raised, allowing for the escalation of actions via the Sentinel framework. Different actions can be assigned to different state outcomes.
Default to Other States: A Default State can transition to a Min Exceeded State or a Max Exceeded State.
Min Exceeded to Other States: A Min Exceeded State can transition to a Max Exceeded State, or to a Default State.
Max Exceeded to Other States: A Max Exceeded State can transition to a Min Exceeded State, or to a Default State.
Test Outcomes
A number of outcomes are possible when the Min Max process is executed:
| Default State | Data is not in an erroneous state (i.e. it is not below the minimum limit or above the maximum limit). |
| Max Exceeded State | Data is greater than the maximum limit. |
| Min Exceeded State | Data is less than the minimum limit. |
| Suppressed State | The monitor has been suppressed. For example, if a precondition has not been met. |
Conditional Logic
The Min Max process provides the following conditional logic.
Note: All of the example graphs in the following sections show tests that have used the Last Known Value sample method.
Max Limit Monitoring
The monitor item is monitored for a maximum limit only.
If the item value exceeds the value defined in Max, a max exceeded event occurs and a max exceeded state is reached.
The following graph shows a possible scenario for a monitor item using Max Limit Monitoring.
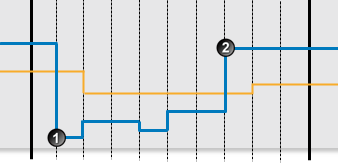 |
The following events are depicted in the graph:
| Data is below the max limit. A default state is reached, and a default event is raised. | |
| Data is above the max limit. A max exceeded state is reached, and a max exceeded event is raised. |
Min Limit Monitoring
The monitor item is monitored for a minimum limit only.
If the item value exceeds the value defined in Min, a min exceeded event occurs and a min exceeded state is reached.
The following graph shows a possible scenario for a monitor item using Min Limit Monitoring.
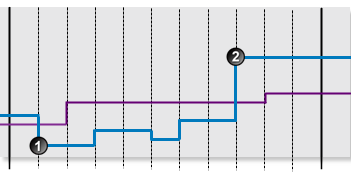 |
The following events are depicted in the graph:
| Data is below the min limit. A min exceeded state is reached, and a min exceeded event is raised. | |
| Data is above the min limit. A default state is reached, and a default event is raised. |
Min and Max Limit Monitoring
Here the item is monitored for minimum and for maximum limits on entities.
If the item value exceeds Max, then a max exceeded state is reached. If the value is lower than Min, then a min exceeded state is reached.
The following graph shows a possible scenario for a monitor item using Min and Max Limit Monitoring.
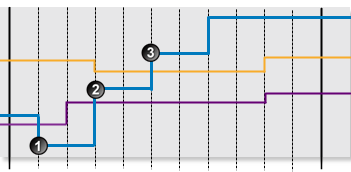 |
The following events are depicted in the graph:
| Data is below the min limit. A min exceeded state is reached, and a min exceeded event is raised. | |
| Data is above the min limit, but below the max limit. A default state is reached, and a default event is raised. | |
| Data is above the max limit. A max exceeded state is reached, and a max exceeded event is raised. |
Adding a Min Max Process
Every test uses a specific type of process, and each process has different limits to define; some of these limits are optional.
The Min Max Process is used for testing continuous data for a monitor item.
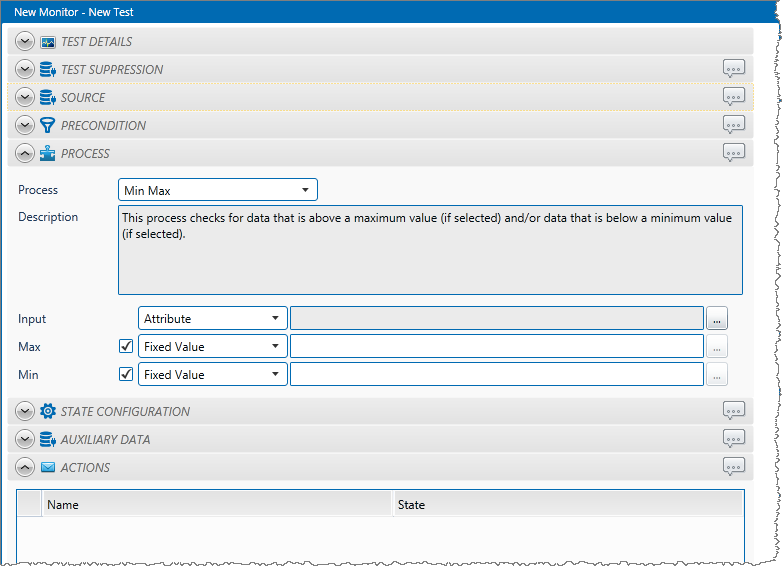
1. In the Process drop-down list, select Min Max.
2. From the Input drop-down list, select an input from the following:
Attribute: This option is only available if the Source Type is Entity or Hierarchy.
Click the ellipsis ![]() button to select an attribute. You are limited to selecting an attribute of the test source monitor items. This attribute of each of the monitor items is a separate process input.
button to select an attribute. You are limited to selecting an attribute of the test source monitor items. This attribute of each of the monitor items is a separate process input.
Source Tag: This option is only available if the Source Type is Tag. If you select this option, then each of the tag monitor items is used as separate process input.
Calculation: Click the ellipsis ![]() button to open the Edit Calculation window.
button to open the Edit Calculation window.
- If the Source Type is Entity or Hierarchy: Type a calculation, prefixed by ‘this’ as the Source Entity token, for example: {this:THP} + 34.
- If the Source Type is Tag: Type a calculation, prefixed by ‘this’ as the Source Tag token, for example: {this} * 2.
Entity Attribute: Click the ellipsis ![]() button to select an entity. From here, select an attribute, or attribute value, for the selected entity.
button to select an entity. From here, select an attribute, or attribute value, for the selected entity.
3. With a Min Max process, you can choose to define a maximum limit, a minimum limit, or both.
To define a Maximum limit:
- Select the Max check box.
- Specify the Max value (see “Available Min and Max Values” below).
To define a Minimum limit:
- Select the Min check box.
- Specify the Min value (see “Available Min and Max Values” below).
Note: At least one test limit, Min or Max, must be specified for this process.
4. To add comments to the process panel click the comment ![]() button, at the top right of the panel.
button, at the top right of the panel.
Available Min and Max Values
These are the values that you can specify for Min or Max:
- Fixed Value: Type in a numerical value.
- Attribute: This option is only available if the test’s Source Type is Entity or Hierarchy. Click the ellipsis
 button to select an attribute of the source entities.
button to select an attribute of the source entities. - Source Tag: This option is only available if the Source Type is Tag.
- Calculation: Click the ellipsis
 button to open the Edit Calculation window.
button to open the Edit Calculation window. - If the Source Type is Entity or Hierarchy: Type a calculation, prefixed by ‘this’ as the Source Entity token, for example: {this:THP} + 34.
- If the Source Type is Tag: Type a calculation, prefixed by ‘this’ as the Source Tag token, for example: {this} * 2.
- Tag: Click the ellipsis
 button to select a tag.
button to select a tag. - Entity Attribute: Click the ellipsis
 button to select an entity. From here, select an attribute, or attribute value, for the selected entity.
button to select an entity. From here, select an attribute, or attribute value, for the selected entity.
Configuring States
For the Min Max process, you can configure the following states, each with an optional state override and comments:
- Max Exceeded
- Min Exceeded
- Suppressed
You cannot change the severity of the Default state; however, you can add a state override and comments.
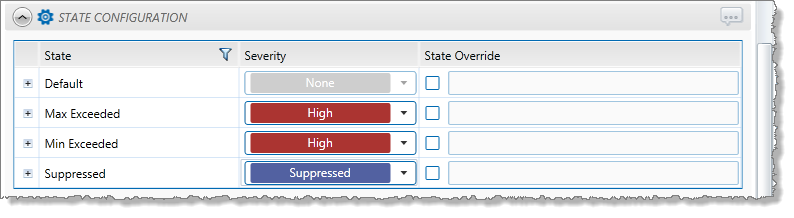
Note: Only configure states where you have set a limit.