ON THIS PAGE:
![]()
P2 Server 4.4 is the engine that powers data retrieval from a variety of disparate sources, with built-in relationship models based on a Data Dictionary. P2 Server is how you get your data, transform it into more useful data, and then serve it up to other applications such as P2 Explorer or P2 Sentinel, for further analysis.
Release 4.4 heralds better, faster connectivity and performance than its predecessors and a rich new set of features in the management tool for simplified data configuration.
Links/Table of Contents
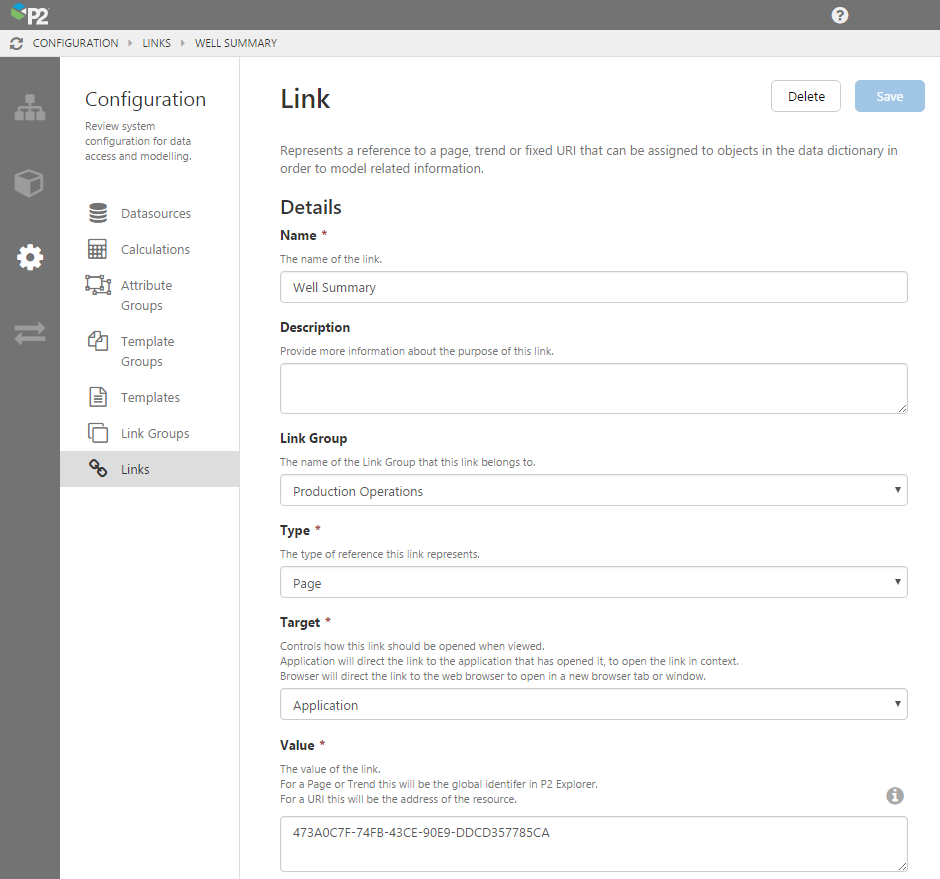
P2 Server 4.4 allows administrators to create links to Explorer pages, trends, and external websites. Links are assigned to templates so that entities can display a Table of Contents in P2 Explorer, which is displayed in the ribbon and is accessible via the hierarchy navigator.
If a link is designated as the primary link on a primary template, it will be regarded as the default link and can be opened using CTRL+click on an entity in the hierarchy, in P2 Explorer.
Server Management
P2 Server 4.3.0 introduced a new enterprise management tool to simplify administration of P2 Server. This tool has been enhanced in successive releases to allow administrators to create and manage datasources, datasets, tags, entities, hierarchies, templates, attributes, and calculations.
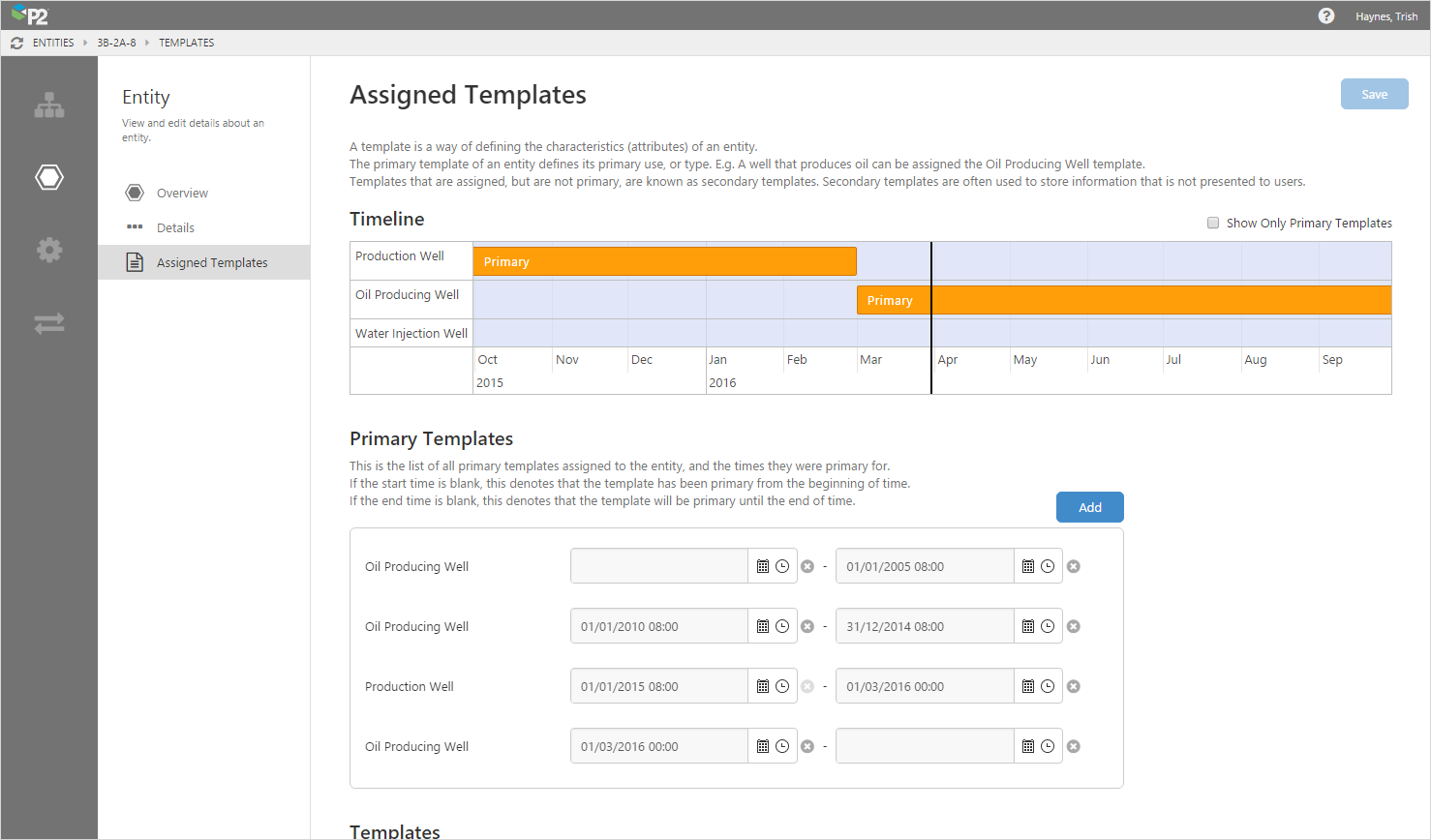
Server Management now also comes with an integrated bulk configuration tool, allowing configurations to be imported and exported with ease.
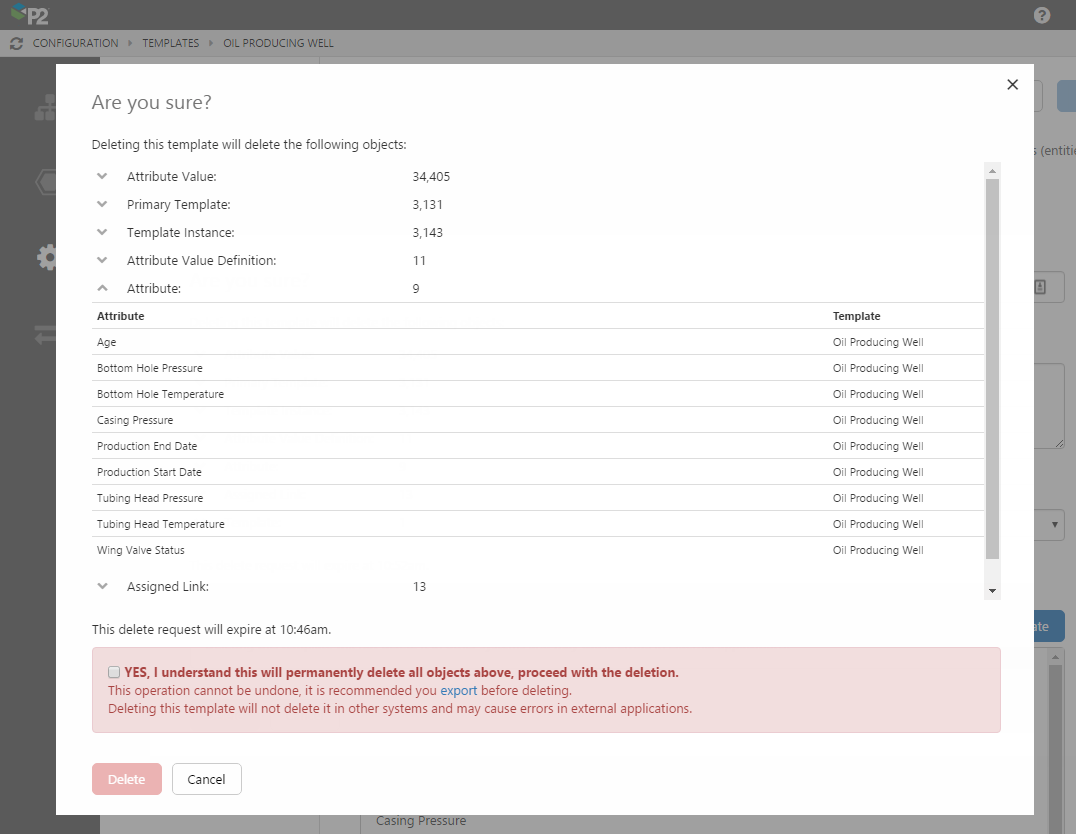
Cascaded Delete
P2 Server 4.4 provides a safe way of deleting objects from the Data Dictionary. When someone attempts to delete an object, such as a template, they are shown a list of other objects that will also be deleted via this operation.
As this action can have unintended consequences, an additional confirmation step ensures that the user cannot accidentally delete objects.
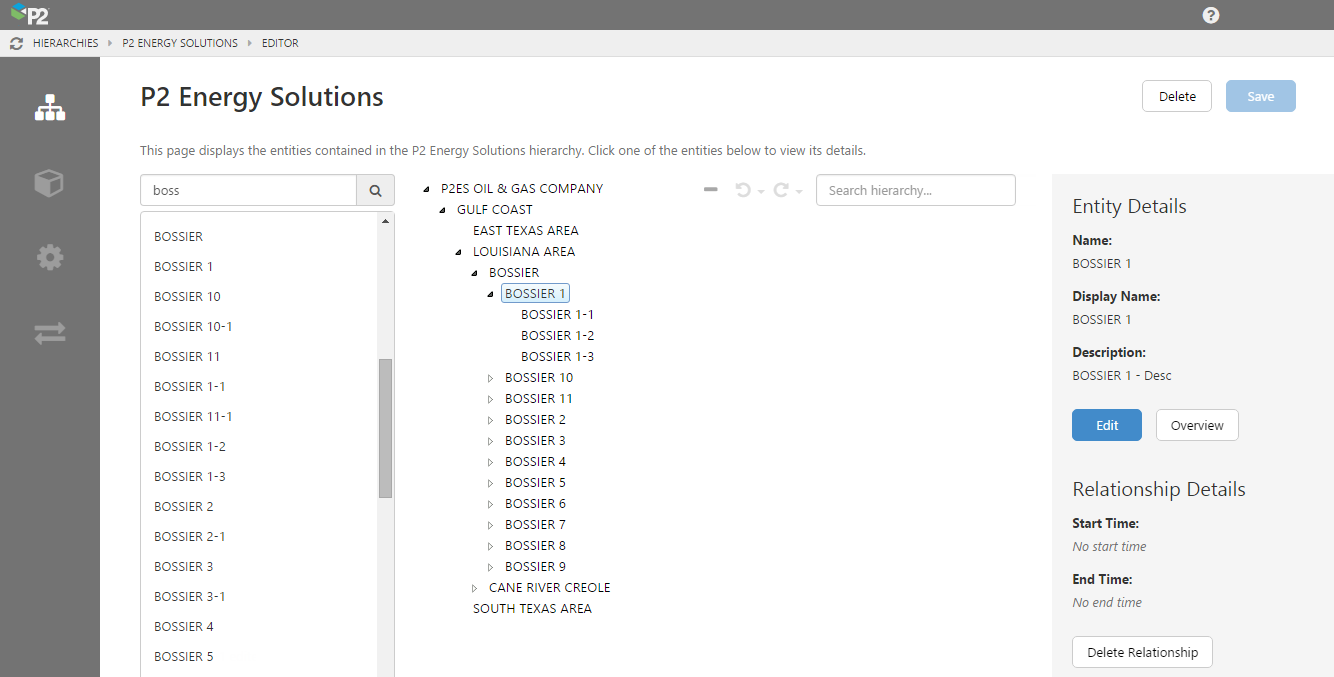
Hierarchy Configuration
P2 Server 4.4 provides a new way of configuring entity hierarchies using drag and drop. Administrators can search for entities and drag them into the hierarchy. Entities can also be moved around within a hierarchy to create the required structure.
Clicking an entity in the hierarchy displays its details in a panel on the right, from which you can edit the entity if required. This panel also displays when the node was active in the hierarchy (currently this can only be set using the import/export spreadsheet).
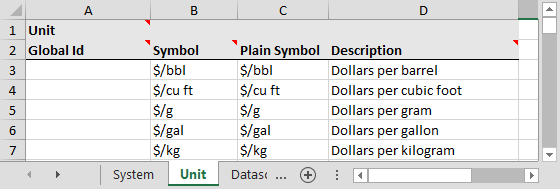
Units
P2 Server 4.4 provides the ability to configure units of measurement in the import/export spreadsheet. A unit can be associated with a tag to define the unit of values fetched from a historian.
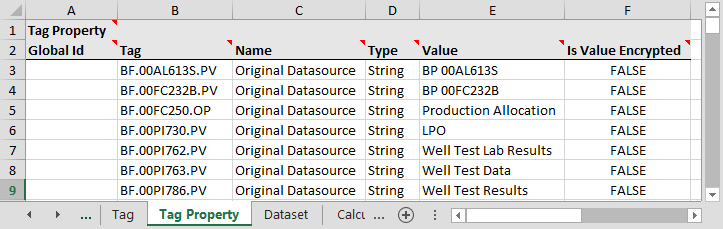
Tag Metadata
P2 Server 4.4 provides the ability to add additional custom properties of a tag, not included elsewhere in the system. This is done using the import/export spreadsheet. The purpose of tag properties is to cater for additional metadata that historians send back with tags, which differs according to historian.
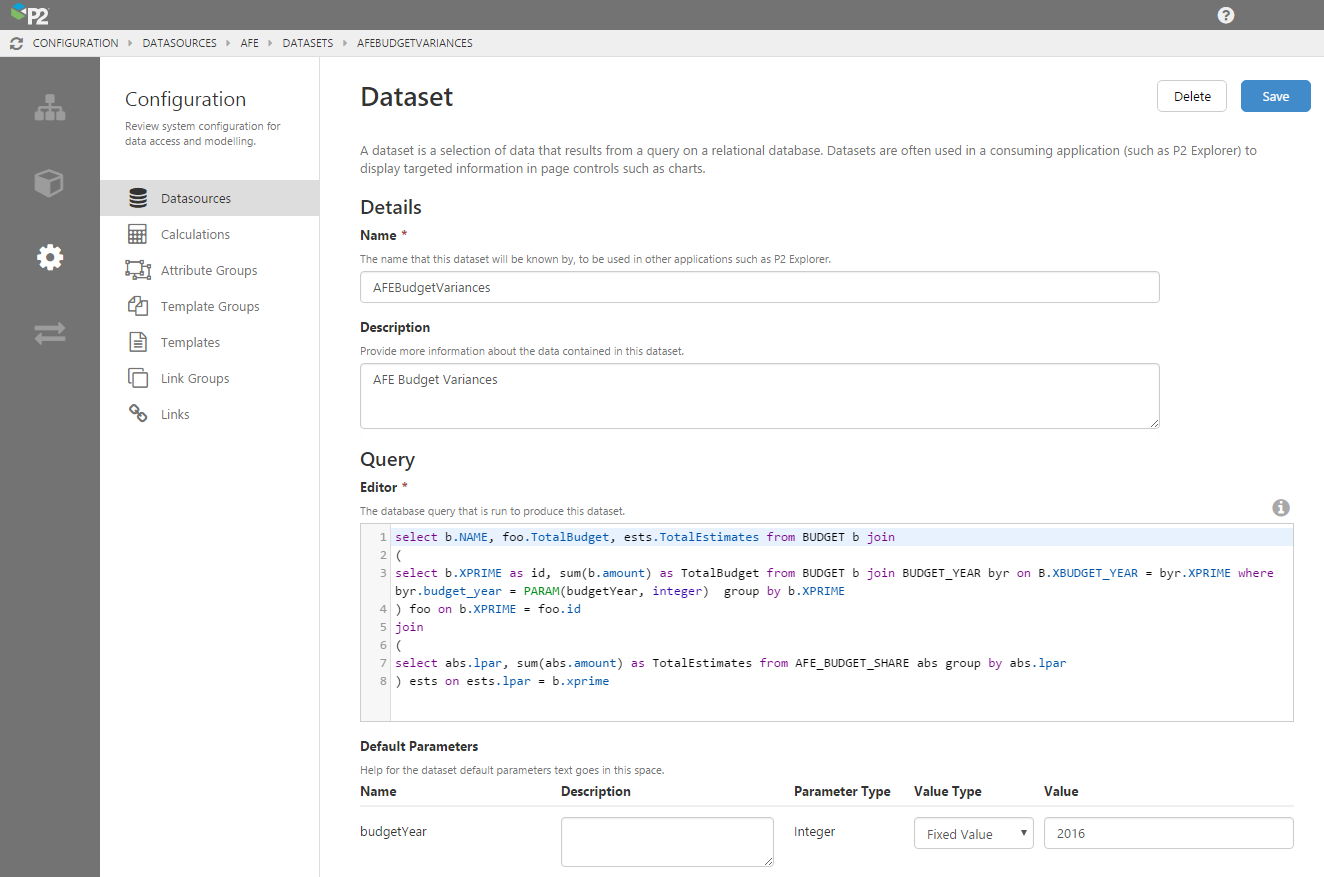
Dataset Default Parameters
P2 Server 4.4 provides the ability to set defaults for parameters in dataset queries. These defaults are propagated to P2 Explorer so that components can automatically pre-fill the parameters during page design, which makes building pages a lot faster.
As you type your query, parameters using the PARAM or PARAMS keywords are automatically added below the query box. E.g. PARAM(budgetYear, integer). You can then assign default values to the parameters, which will automatically propagate to P2 Explorer when the query is used on a page.
Adaptors
P2 Server provides a range of adaptors, which enables data to be collected from external sources. Adaptors are specific to the type of system they connect to. The following adaptors are currently available in P2 Server 4.4:
- P2 Server 2.6 Adaptor – connects to the P2 Explorer 2.6 data dictionary and provides the provides the ability to fetch tag data from datasources already configured in P2 Explorer 2.6.
- PI Adaptor – connects to the OSIsoft PI Historian and supports version 3 of the PI Server. It provides the ability to read and write time series tag data to and from the historian.
- Relational Adaptor – allows data from relational databases to be transformed into time series data, and provides the ability to read and write data to and from the database.
- Proficy Adaptor – connects to the GE Proficy Historian and provides the ability to read and write time series tag data to and from the historian.
- PHD Adaptor – connects to the Honeywell Uniformance PHD R300 Historian, and provides the ability to read and write time series tag data to and from the historian.
ODBC and Write Support in Relational Adaptor
The Relational Adaptor allows data from relational databases to be transformed into time series data. In addition to native support for Oracle and SQL Server databases, release 4.4 introduces support for ODBC and writeable tags.
The addition of ODBC includes support for both narrow and wide queries.
Writeable tags can be used to store processing results which can then be used for further processing in some way (e.g. calculations, trending, Sentinel processes).
API
P2 Server 4.3.1 introduced a new .Net Client to connect to P2 Server, providing one access point to all API endpoints, including the Data Broker and Data Dictionary APIs as well as P2 Security. This allows developers of consuming applications to more easily fetch data and hierarchies from P2 Server. The client reduces the need for complex code and provides an easy to use wrapper for P2 Security.
Other features include:
- Security token refreshing and caching
- Defaults are automatically applied
- Thread-safety built-in
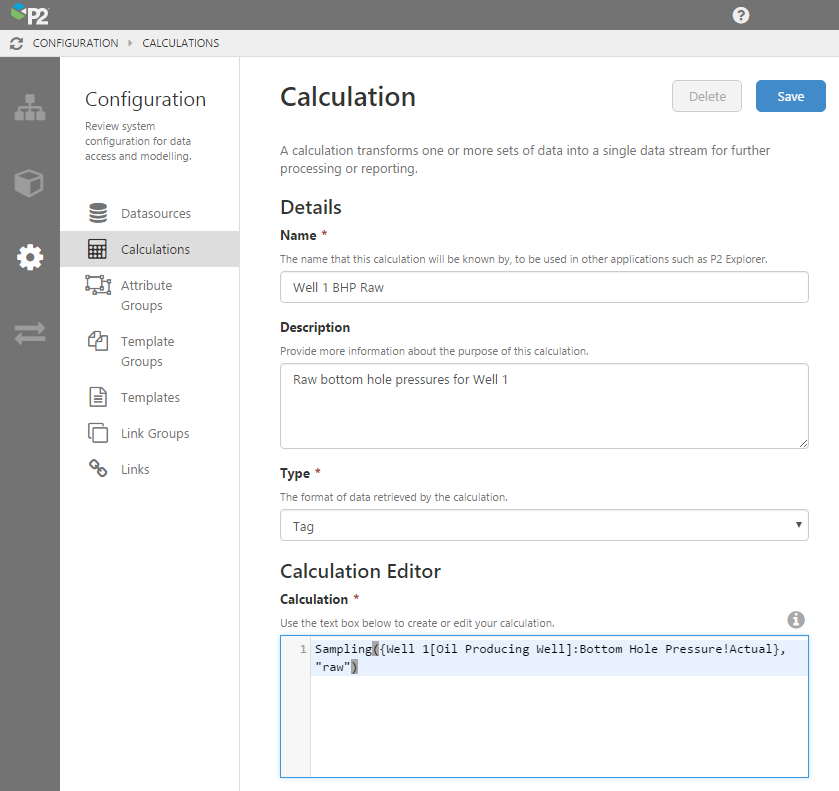
Calculations
P2 Server 4.3.2 included all calculations previously available in P2 Explorer 2.6. Additionally, the following new functions were introduced:
- 6 new casting functions (Boolean, DateTime, Decimal, Duration, Integer, String)
- CatchLowConfidence
- StdDev
- StdDev_Sampled
P2 Server also provides an interface for creating calculation expressions in P2 Server Management. Calculations can be saved for use in applications such as P2 Explorer.
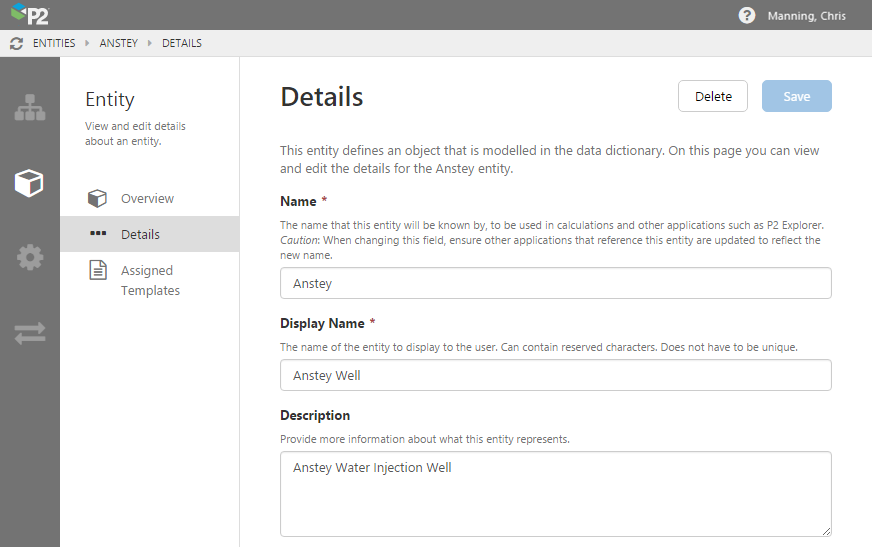
Display Names
P2 Server 4.3.1 introduced support for duplicate entity names through the use of display names and internal names. This allows P2 Server to refer to existing entities from another system (such as ProCount, Enterprise Upstream) using the same names that they are known by in that system.
External systems are identified with a unique name in P2 Server, and entities from that system are mapped with a display name. This system mapping allows P2 Server to display entity names in a hierarchy in the same way that they are displayed in the source system – even if the names are duplicates.
It is up to system configurators to match up entities in P2 server with the corresponding entities in the external system, using a combination of the system ID and the entity ID from that system.
Time-Aware Hierarchies
P2 Server 4.3.0 introduced support for hierarchies to change over time. This means that as items are moved in the hierarchy, or added and deleted, this history is now all recorded and can be used to more accurately depict the real state of real world items that exist on site, at a given point in time.
In the future, this hierarchy and its new time-aware features will be supported for use inside calculations. This enables powerful hierarchical calculations such as, “Sum up the ‘Total Oil Produced’ amounts from all ‘Wells’ in ‘Field A’ for Jan 2014”. This will make rollup-style calculations much easier, and will also be smart enough to not include wells that did not exist in the hierarchy at the time.
Comment Infrastructure
P2 Server 4.3.0 introduced the infrastructure for applications to create and save threaded comments.
The comments infrastructure enables comments to be applied to a specific date or date range. Comments can therefore be for a point in time or for a period (e.g. reporting month).
Comments can also be given a “context”, which can later be used for filtering.
Previous Releases