ON THIS PAGE:
P2 Explorer uses roles to assign privileges to a user. All users with a particular role will inherit the privileges assigned to that role.
In order to be able to assign roles, a user must be a Security administrator.
Default Roles
When P2 Explorer is first installed, there are two default roles: Administrators and Everyone.
- By default all users are assigned to the Everyone role, which has read access to all resources.
- Only the default admin user is initially assigned to the Administrators role, which provides administration privileges over all modules. Even though these privileges are added by default, they can be changed and deleted without affecting the functionality of P2 Explorer.
Resource Role Privileges Matrix
When we talk about role privileges as seen on the Role Privileges page in Server Management, we are specifically talking about module and resource level privileges and that is what this article will focus on.
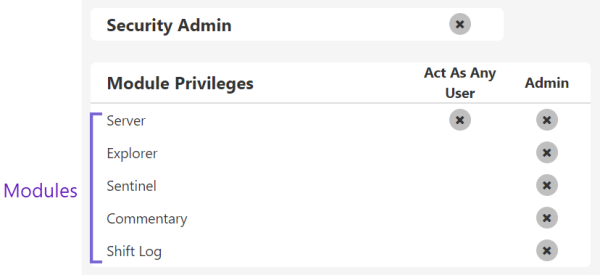
Module level privileges provide administrative access to all resources and objects for a particular module. A module is the part of the software that allows P2 Explorer to provide various capabilities. For example:
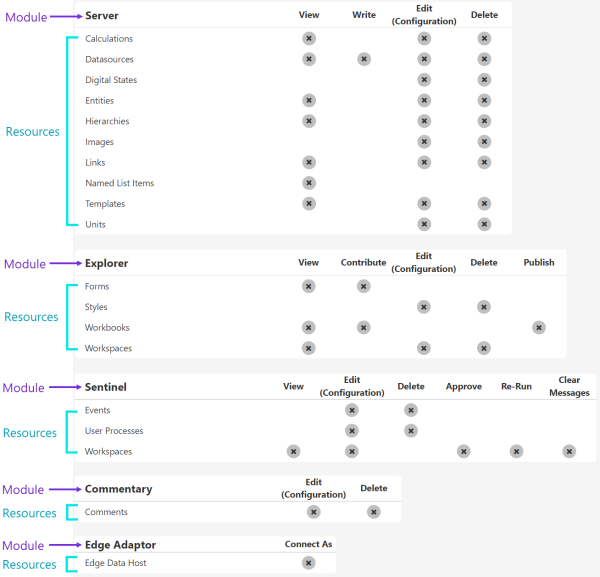
- Server: Makes the Data Dictionary and administrative functions available to other modules.
- Explorer: Provides page and trend visualisations of live and historical data.
- Sentinel: Makes Sentinel events available for analysis.
- Commentary: Provides commentary capability to P2 Explorer.
- Shift Log: Captures shift based operational information.
A resource is a collection of a particular type of object, such as workspaces. Each module has a set of resources that represent discrete objects within a module. E.g. The Explorer module has forms, styles, workbooks and workspaces resources.
The type of privilege that can be applied to a resource depends on the module - e.g. most resources have View privileges, but only the Sentinel module provides the Re-Run privilege on its workspaces resource.
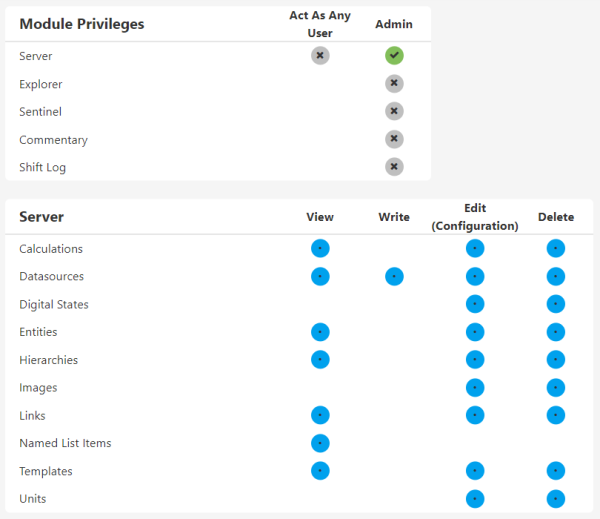
Assigning Module Privileges
When you assign a module level privilege - i.e. an Admin privilege - the corresponding resources in that module all inherit all of the privileges. The resource privileges show a blue circle with a dot. You cannot further refine the resource privileges because the module privilege overrides the resource privilege.
Assigning Resource Privileges
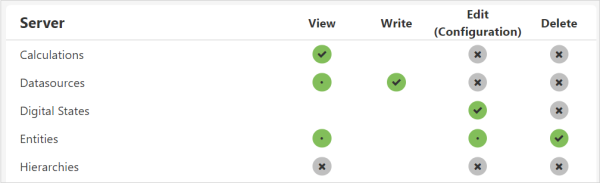
You can assign resource privileges without a module level privilege by directly clicking the privilege against the resource. Note that privileges cascade here too, with the highest level privilege generally on the right, and the lowest on the left. When you assign a high level privilege, such as Delete, lower level privileges are also automatically granted when that privilege is required to perform the action. This is shown by a green circle with a dot.
What the Colours Mean
The privileges matrix is colour-coded to indicate the cascading nature of privileges. The colours are:
![]() Grey: Privilege not granted
Grey: Privilege not granted
![]() Green tick: Privilege is explicitly granted, associated privileges will also be automatically granted.
Green tick: Privilege is explicitly granted, associated privileges will also be automatically granted.
![]() Green dot: Privilege is granted because a higher level privilege has been granted on the resource.
Green dot: Privilege is granted because a higher level privilege has been granted on the resource.
![]() Blue: Privilege is granted because it is inherited from a module privilege.
Blue: Privilege is granted because it is inherited from a module privilege.
Release History
- How Roles Work (this release, 4.9.1):
- Shift Log Administration Module